In programming, we have 4 ways of defining a function and they are :-
-
Takes something and returns something.
-
Takes something and returns nothing.
-
Takes nothing and returns something.
-
Takes nothing and returns nothing.
A class in C++ can have all the 4 above mentioned types of member functions as per requirement.
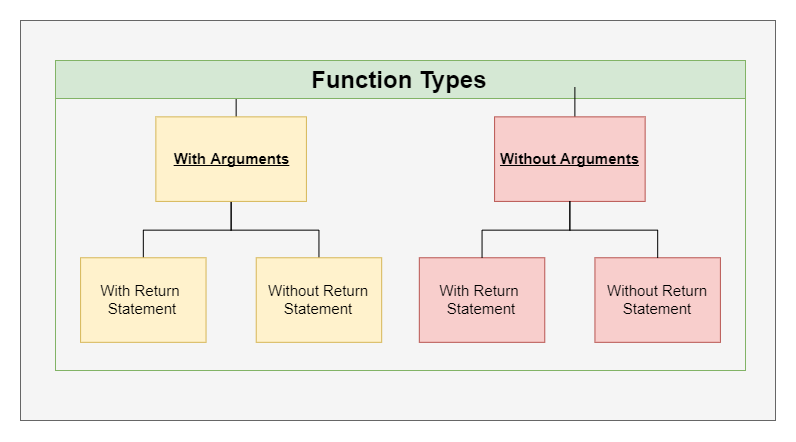
Types of Function
Syntax :
// Function Declaration - takes nothing and returns nothing
void funtion1();
// Function Declaration - takes nothing and returns something
int funtion2();
// Function Declaration - takes something and returns nothing
void funtion3(int a, int b);
// Function Declaration - takes something and returns something
int funtion4(int a, int b);
Example :
// Simple Function Types Example Program in C++
// Function Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void funtion1(); // Function Declaration - takes nothing and returns nothing
int funtion2(); // Function Declaration - takes nothing and returns something
void funtion3(int a, int b);
int funtion4(int a, int b); // Function Declaration - takes something and return something
int main() {
int x, y;
cout << "Simple Function Types Example Program in C++ \n";
// Function Call - takes nothing and returns nothing
funtion1();
// Function Call - takes nothing and return something
x = funtion2();
cout << "\nReturnValue: " << x;
// Function Call - takes nothing and returns nothing
funtion3(10,20);
// Function Call - takes nothing and return something
y = funtion4(100, 200);
cout << "\nAddition: " << y;
return 0;
}
void funtion1() // Function Definition - takes nothing and returns nothing
{
cout << "\nIt's simple function definition";
}
int funtion2() // Function Definition - takes nothing and return something
{
int c = 1000;
return c;
}
void funtion3(int a, int b) // Function Definition - takes something and returns nothing
{
int c;
c = a + b;
cout << "\nAddition: " << c;
}
int funtion4(int a, int b) // Function Definition - takes something and return something
{
int c;
c = a + b;
return c;
}
Output :
Simple Function Types Example Program in C++
It's simple function definition
Return Value: 1000
Addition: 30
Addition: 300

